IoTeX Tokenomics — Part 2: DAO-Based Tokenomics

Welcome to the IoTeX Tokenomics series. In Part 1, we explained the utility of the IOTX coin. In Part 2, we introduce the underlying technical principles. In Part 3, we will share how the “Powered by IoTeX” ecosystem will be bootstrapped.
The IoTeX platform is a canvas for builders, service providers, and consumers to interact in a decentralized fashion. As the currency of the IoTeX Network, the IOTX coin plays a critical role to promote fairness, incentivize cooperation, and ensure interactions between network participants are trusted. However, as a “medium of exchange” the IOTX coin cannot single-handedly guarantee network-wide trust. In addition, smart contracts that define and enforce the operating rules of the IoTeX Network, especially how value and information flows between network participants, play a critical role in ensuring a fair, transparent, and trusted ecosystem.
To achieve a decentralized network, the components of the network must also be decentralized, including governance, consensus, and tokenomics. Decentralization and “radical transparency” are first principles of the IoTeX Network and are embedded into our tokenomics design. In this article, we explain how IoTeX applies DAO-based tokenomics to enable builders, service providers, and consumers to interact with guaranteed trust.
What is a DAO?
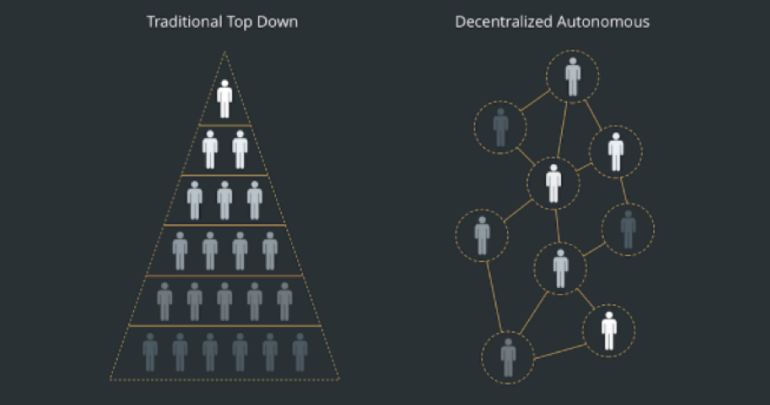
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is a set of smart contracts running on a blockchain that coordinate multiple parties to achieve a specific goal. DAOs mimic traditional organizations — both are trusted by diverse stakeholders (that do not necessarily trust each other) to facilitate multi-party processes. However, what differentiates DAOs from traditional organizations is their decentralized and autonomous properties. This can be best explained by breaking down each term:
- Decentralized: DAOs are not organized hierarchically or controlled by any single entity; rather, they are openly accessible and governed in a distributed manner.
- Autonomous: the operating rules of a DAO are not subject to interpretation; rather, business logic is auto-enforced by programmable smart contracts after predefined conditions are met
- Organization: DAOs are digital representations of traditional organizations, which have a common purpose, coordinated effort, division of labor, and trusted authority.
The decentralized and autonomous properties of DAOs protect them from external and internal errors and attacks — in other words, no single entity can stop, change, or manipulate a DAO. This concept is being explored across the blockchain industry for insurance, finance, art, and more. In the IoT space, DAOs will play a critical role to coordinate trusted interactions between a large number of humans and machines.
DAO-Based Tokenomics
The IoTeX Network utilizes DAOs to facilitate “burn-to-certify” and “stake-to-service” tokenomics operations in a transparent and decentralized manner. To ensure verifiability and equal access for all network participants, IoTeX DAOs will be open-source and accessible by anyone (i.e., permission-less). After a DAO is deployed on the IoTeX Network, cryptocurrencies (e.g., IOTX, NFTs), crypto-assets (e.g., DID, VC), and other information may be deposited and submitted to the DAO, which will then trigger actions based on pre-programmed rules.
In the rest of this section, we explain the underlying design of the IoTeX DAOs that will facilitate “burn-to-certify” and “stake-to-service” tokenomics operations.
“Burn-to-Certify” DAO
IoTeX builders (i.e., device manufacturers) will burn IOTX in order to obtain a “Powered by IoTeX” (PBI) Certificate, which grants a device access to special services and capabilities. Although PBI certificates are especially useful for device manufacturers (e.g., Tenvis), any IoTeX user will be able to obtain one for their devices in a permission-less fashion by meeting specified requirements. In the graphic below, we outline the process flow regarding how builders and devices interact with the “Burn-to-Certify” DAO for device registrations.

- Builder submits device information (e.g., manufacturer name/VC, model #) to “Device Registration Smart Contract” and receives a “Proof of Registration”.
- Builder deposits IOTX and submits their validated “Proof of Registration” to “Burn Smart Contract” and receives a “Proof of Burn”.
- Each DID with an associated “Proof of Registration” and “Proof of Burn” will receive a “Powered by IoTeX” Certificate.
- Devices with a “Powered by IoTeX” Certificate may access PBI services on the IoTeX Network.
Based on this “Burn-to-Certify” design, the total supply of IOTX will decrease with every new “Powered by IoTeX” device (e.g., Ucam), while also driving increased activity in the IoTeX Network and value for the IOTX coin. Please see Tokenomics Part 1 for more information on the device registration utility of the IOTX Coin.
“Stake-to-Service” DAO
Service providers (e.g., Filecoin for storage, Helium for connectivity, NKN for P2P networking) will be required to stake IOTX to obtain the right to provide services to “Powered by IoTeX” devices. This process also requires each service provider to define and submit information regarding their services — this includes service level agreements (SLAs) that detail their specific quality/availability guarantees, as well as remediation for violating these SLAs. In the graphic below, we outline the process flow regarding how service providers interact with devices, builders, and the “Stake-to-Service” DAO.

- Service Provider submits information regarding their service (e.g., description, SLAs, remediation) to “Service Provider Registration Smart Contract” and receives a “Proof of Registration”
- Service Provider stakes IOTX and submits “Proof of Registration” to “Service Provider Staking Smart Contract” and receives a “Proof of Stake”
- Each Service Provider with an associated “Proof of Registration” and “Proof of Stake” will have the right to deliver services to “Powered by IoTeX” devices
- Builders (i.e., device manufacturers) will pay the Service Provider for their services. The Service Provider may define how they wish to receive payment, whether that is in IOTX, fiat, or other cryptocurrencies.
- Service Providers will be required to periodically submit service level reports, which may be compared to the Service Provider’s predefined SLAs. If any SLAs are breached, the builder (i.e., device manufacturer) will receive remediation based on the terms set by the Service Provider
This “Stake-to-Service” model has no direct impact on the total supply of IOTX, but as more “Powered by IoTeX” devices are onboarded, more service providers will stake to join and drive increased activity in the IoTeX Network and value for the IOTX coin. Once enough service providers are in place for each category of service (e.g., storage, connectivity, compute), we will implement a bidding layer on top of this “Stake-to-Service” model, as well as a reputation-based system to ensure Service Providers are trustworthy. Please see Tokenomics Part 1 for more information on the “stake-to-service” utility of the IOTX Coin.
What’s Next?
As the Internet of Trusted Things comes to life with the first blockchain-powered IoT products like Ucam and Pebble Tracker, the potential impact of IoTeX has never been greater. Furthermore, the roles of various network participants — builders, service providers, consumers — and the spectrum of interactions between them are evolving by the day. With the upcoming launch of Ucam to mass market retailers in early Q3 2020, Ucam will serve as the first vehicle for IoTeX tokenomics and drive new value and utility to the IoTeX Network.
As detailed in this article, the IOTX coin, complementary DAOs, and IoTeX’s overall tokenomics design serve as catalysts for the Internet of Trusted Things. However, IoTeX has more exciting plans to bootstrap (i.e., go from 0 → 1) the “Powered by IoTeX” ecosystem. Stay tuned for Part 3 of our Tokenomics series, where we will share how the next wave of “Powered by IoTeX” devices will be onboarded via reserved Ecosystem funds.
About IoTeX
Founded as an open source platform in 2017, IoTeX is building the Internet of Trusted Things, an open ecosystem where all “things” — humans, machines, businesses, and DApps — can interact with trust and privacy. Backed by a global team of 30+ top research scientists and engineers, IoTeX combines blockchain, secure hardware, and confidential computing to enable next-gen IoT devices, networks, and economies. IoTeX will empower the future decentralized economy by “connecting the physical world, block by block”.
IoTeX Blogs
Subscribe to get the latest posts from IoTeX Blogs delivered to your inbox.